Our brain is the most vital organ of our body which keeps functioning throughout life without rest. There are some other organs also who do not take a rest and one of the greatest examples of this is our heart. It cannot take a rest for even a single moment. Still when we see the total picture of human anatomy and physiology then we find that the brain is far more complex and sophisticated than all other organs including our heart. So much is that it will be utterly blunderous to even compare the brain with any other organ or system within our body.
Being so complex and sophisticated, being so active and busy, and being perfect to perform, our brain needs a lot of resources. Among those resources, food and nutrition or you may say calorie and nutrition is a large issue. And vitamins also belong to the category of nutrition, and some vitamins are more than important for the brain. Vitamin B is exactly such a vitamin.
Before proceeding on how vitamin B can help us by helping our brain, it will be better to know about the vitamin for better understanding.
There are 13 vitamins that our body needs on a regular basis as nutrients, or micronutrients to be precise. Vitamins are called micronutrients because they are required by our body in a very minute quantity, usually at the scale of micrograms. Macronutrients like protein, carbohydrates and fats are required in the scale of grams, actually speaking 10s of grams. This is where vitamins differ from the macronutrients in respect to quantity.
Among those 13 vitamins, there are 2 categories, viz. fat soluble vitamins and water soluble vitamins. 4 vitamins, vitamin A, D, E and K are fat soluble vitamins. Vitamin C and the 8 vitamins under the group-name of vitamin B are water soluble.
Thus vitamin B is the largest family of vitamins with 8 members. Each member has its own name, composition and functions. The table below gives some details about all the 8 vitamin B.
Fig 1: List of all vitamin B compounds with their functions as human vitamins.
We will discuss our food sources of these vitamins later in this article. Now let us see how beneficial they are especially for our brain and nervous system.
If we see the table in figure 1 meticulously then we can find that many of the members of vitamin B are directly functional for our nervous system.
Cellular metabolism is also a very important issue for brain and nervous system functions. Brain and the nervous system requires a huge amount of energy for its proper functioning.
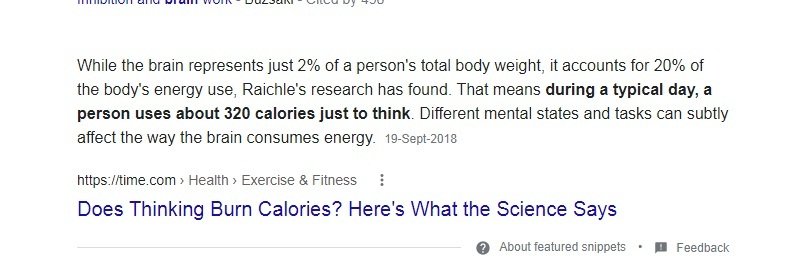
Thus as in Figure 2, we can see that the brain demands more than 20% of the body’s total energy quota. Without proper metabolic functions both at the systemic and cellular levels, it would not be possible to maintain the supply of this huge amount of energy. And almost all the members of vitamin B are crucially vital for the metabolic performances of our body.

This is how indirectly vitamin B is so important for brain and nervous system functions. Other than metabolic benefits, vitamin B directly participates in numerous brain operative and maintenance functions.
The brain needs continuous supply and maintenance of numerous neurochemicals and signaling molecules. There are very complex physiological synthesis processes for this purpose. Vitamin B participates and assists in these synthesis processes of those neurochemicals and signaling molecules. Deficiency of these chemicals can lead to major compromise in brain and neurological performances in various sectors including cognitive performances to ANS and CNS performances including almost all systemic areas of the human body.
When we are specially concerned about students and their academic performances, cognitive performance is directly involved and other systemic functions are indirectly involved to provide all the necessary support. Beside these there are many other functional areas within the brain which are backed up by the B vitamins, which essentially takes care about the health and performances of each nerve and their connections.
Learning is mostly about nerves and their connections in proper order. Without optimum health and performance in this sector, whatever effort a student will give in his or her studies, will invariably go to vain because it will be hard to retain. The retention of whatever we learn is what we call the memory. However hard the brain functions and however effort the student invests, without enough and optimum memory performances, hardly anything will retain.
The functioning and maintenance of nerve and its systems, there are continuous requirements of various protein synthesis beside the provision of energy and brain chemicals as we saw above. Vitamin B facilitates proper synthesis mechanisms for those proteins through various biochemical reaction processes. They also provide better recovery support for both regular wear-and-tear as well as any eventual injury to the brain cells.
More can be written about all the B vitamins and their involvement in our brain and nervous system functions as well as many other physiological systemic functions, both collectively and individually. But we do not have the scope to go that deep here in this article. It will need much space and academic depth which we can keep aside for now.
So now let us see how we can provide optimum vitamin B quantity to the students, teachers and other people who are more and more dependent on their efficiency of brain functions.
